| [1] |
ZHANG Yi, LIANG Zhao-xin.
Visualization of similarity transformation with spin 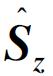 rotating to rotating to  [J]. College Physics, 2023, 42(8): 55-.
[J]. College Physics, 2023, 42(8): 55-.
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Yue-xia, ZHANG Xiao-long.
Further exploration on time dilation effect
[J]. College Physics, 2023, 42(6): 28-.
|
| [3] |
HU Xiang-ming.
Connecting role of 4-velocity in special relativity
[J]. College Physics, 2023, 42(3): 9-.
|
| [4] |
GONG Yi-hong.
An approximate calculation of candle powered turbine’s torque
[J]. College Physics, 2023, 42(11): 48-.
|
| [5] |
ZHANG Hui-jun, ZHANG Yan, WU Jie, FENG Xue-chao, WANG Shi-zhuo.
Dynamics analysis of sliding down time affected by resistance
[J]. College Physics, 2023, 42(05): 31-.
|
| [6] |
LIN Zheng-zhe, CHEN Xi.
Discussion on orbit angular momentum and rotation momentum in classical mechanics
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(8): 15-.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Hui-jun, CHEN Jing, JIANG Feng-chun, WANG Shi-zhuo.
The solution to rotational inertia of uniform Reuleaux polygon sheet
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(6): 26-.
|
| [8] |
ZHAO Song-nian, LU Bo, CHEN Ken, HUANG Xu .
The analogy between fiber bundle,gauge field and Yang-Mills equation—A way of disciplinary integration research
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(6): 16-.
|
| [9] |
LIU Shu-jing, CHU Xin-wei, LUO Ming-yan, JI Qiang, JU Dan-dan, LIU Jun-yu, WANG Da-shen, XIE Ming-nian.
Exploration ofideological and political education in space-time view of special relativity
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(4): 44-.
|
| [10] |
LUO Xin-rui, YU Cong.
The internal structure of the rotational polytropes
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(10): 59-.
|
| [11] |
WANG Lei.
Some problems in the teaching of special relativity
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(1): 24-.
|
| [12] |
FANG You-le, WANG Tian-xiao.
Analysis of the rotation modes of the coin under different conditions
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(1): 61-.
|
| [13] |
ZHAO Dong-qiu, JIA Shuan-wen, QIN Xu-ming, YUAN Di, DONG Hao .
The critical angular velocity of a rotating spring on a horizontal plane
[J]. College Physics, 2022, 41(07): 19-.
|
| [14] |
XIAO Tian-ning, WANG Shuan-hu.
Electrodynamic explanation of faraday magneto-optical rotation effect
[J]. College Physics, 2021, 40(9): 72-.
|
| [15] |
LIN Jiong-hui¹, LIU Yu-ying², SONG Min².
Three-dimensional simulation and visualization of the motion of rigid body and
discussion
on physical pendulum related problems
[J]. College Physics, 2021, 40(7): 68-.
|